LM operates a parcel delivery service. Last year its employees delivered 15,120 parcels and travelled 120,960 kilometers. Total costs were $194,400.
LM has estimated that 70% of its total costs are variable with activity and that 60% of these costs vary with the number of parcels and the remainder vary with the distance travelled.
LM is preparing its budget for the forthcoming year using an incremental budgeting approach and has produced the following estimates:
• All costs will be 3% higher than the previous year due to inflation
• Efficiency will remain unchanged
• A total of 18,360 parcels will be delivered and 128,800 kilometers will be travelled.
Calculate the following costs to be included in the forthcoming year’s budget:
(i) the total variable costs related to the number of parcels delivered.
(ii) the total variable costs related to the distance travelled.
JRL manufactures two products from different combinations of the same resources. Unit selling prices and unit cost details for each product are as follows:

The optimal solution in the previous question shows that the shadow prices of skilled labour and direct material A are as follows:
Skilled labour $ Nil
Direct material A $11.70
Explain the relevance of these values to the management of JRL.
What is the additional contribution that can be earned?
A decision maker that makes decisions using the minimax regret criterion would be classified as:
THS produces two products from different combinations of the same resources. Details of the products are shown below:
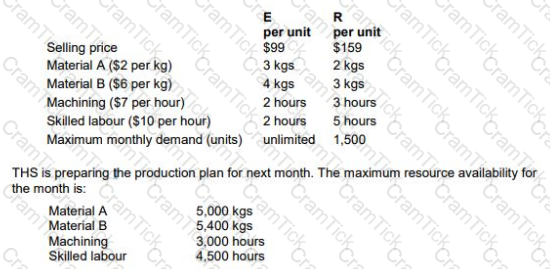
Identify, using graphical linear programming, the optimal production plan for products E and R to maximize THS’s profit in the month.
A budgetary control report for the latest period is shown below:
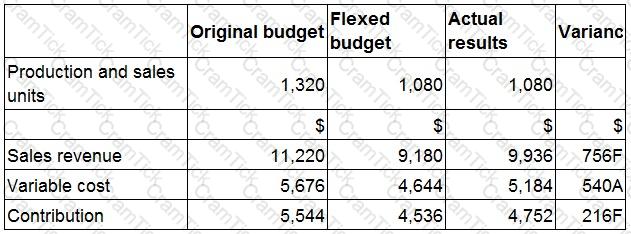
Which TWO of the following statements are correct?
RT produces two products from different quantities of the same resources using a just-in-time (JIT) production system. The selling price and resource requirements of each of the products are shown below:

Market research shows that the maximum demand for products R and T during June 2010 is 500 units and 800 units respectively. This does not include an order that RT has agreed with a commercial customer for the supply of 250 units of R and 350 units of T at selling prices of $100 and $135 per unit respectively. Although the customer will accept part of the order, failure by RT to deliver the order in full by the end of June will cause RT to incur a $10,000 financial penalty. At a recent meeting of the purchasing and production managers to discuss the production plans of RT for June, the following resource restrictions for June were identified:
Direct labour hours 7,500 hours
Material A 8,500 kgs
Material B 3,000 litres
Machine hours 7,500 hours
Assuming that RT completes the order with the commercial customer, prepare calculations to show, from a financial perspective, the optimum production plan for June 2010 and the contribution that would result from adopting this plan.
The optimum production plan will be:
The labour requirement for a special contract is 250 skilled labour hours paid at $10 per hour and 750 semi-skilled labour hours paid at $8 per hour.
At present, skilled labour is fully utilised on other contracts which generate a $12 contribution per hour, after charging labour costs. Additional skilled labour is unavailable in the short term.
There is a surplus of 1,200 semi-skilled hours over the period of the contract but the firm has a policy of no redundancies.
The relevant cost of labour for the special contract is:
Which THREE of the following statements relating to fixed overhead variances are correct?
A healthcare company specializes in hip, knee and shoulder replacement operations, known as surgical procedures. As well as providing these surgical procedures the company offers pre operation and post operation in-patient care, in a fully equipped hospital, for those patients who will be undergoing the surgical procedures.
Surgeons are paid a fixed fee for each surgical procedure they perform and an additional amount for any follow-up consultations. Post procedure follow-up consultations are only undertaken if there are any complications in relation to the surgical procedure. There is no additional fee charged to patients for any follow up consultations. All other staff are paid annual salaries.
The company’s existing costing system uses a single overhead rate, based on revenue, to charge the costs of support activities to the procedures. Concern has been raised about the inaccuracy of procedure costs and the company’s accountant has initiated a project to implement an activity-based costing (ABC) system. The project team has collected the following data on each of the procedures.
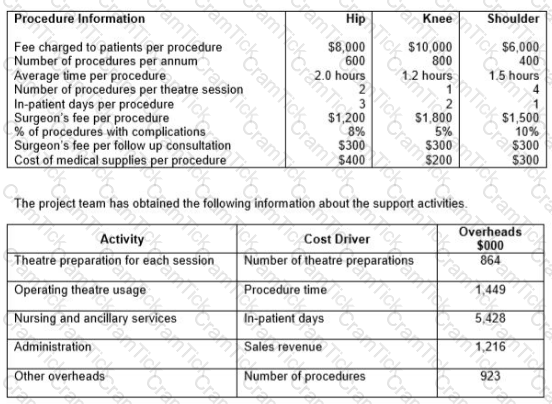
Calculate the profit per procedure for each of the three procedures using activity-based costing.
What was the profit for the knee procedure, using ABC costing?
A museum charges a reduced entrance fee for students in full-time education. The budgeted cost per customer is the same regardless of the entrance fee paid.
4,000 customers were budgeted to visit the museum during period 6, with 25% of customers paying the reduced fee.
3,000 customers visited the museum during period 6 and 1,000 of these paid the reduced entrance fee. Costs were as budgeted but the actual full-priced entrance fee was $2 higher than budgeted.
Which of the following statements is true?
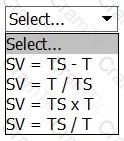
A time series (TS) is made up of two main components i.e. trend (T) and the seasonal variation (SV).
The equation that represents the seasonal variation under the additive model is:
You are a trainee management accountant working for a prestigious manufacturing firm. One day you go to a business meeting a business meeting and the managing director is there. They stand up and say that the
company is losing too much money through wastage and losses and so they have decided to implement a total quality management system. They go on to say this system will:
1:Allow the company to improve on a consistent and continual basis
2:Allow the company to identify and allocate quality accountability to certain departments
3:Help the company detect error and fraud
Are ALL of these statements correct?
A company manufactures a single product. The cost card for a unit of this product is as follows:
During month 6, finished goods inventory increased by 350 units.
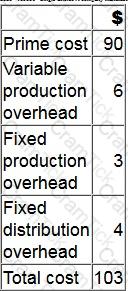
By how much would the profit differ in month 6 if finished goods inventory was valued at standard marginal cost rather than standard absorption cost?
When classifying quality costs, which of the following is NOT likely to be an appraisal cost?
RST is preparing a quotation, on a relevant cost basis, for a special order.
Which TWO of the following are relevant costs that should be included in the quotation?
Which of the statements about allocation of joint costs to products are true and which are false?

A manager in your organisation says, "I have spare capacity and I need a unit cost as a basis for pricing a special one-off contract. You have provided me with a relevant cost of $6.50 per unit and a full production cost of $8.00 per unit. Please explain which unit cost I should use."
Which cost should be used in this decision and why?
A company manufactures a machine. The machine is made from two types of raw material and is assembled in a factory using skilled labour. The engine for the machine is purchased from an outside supplier.
The following costs relate to the manufacture of one machine:
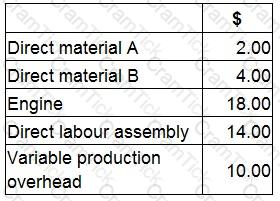
What is the finished goods inventory valuation for one machine using throughput costing?
Which of the following would help to explain a favourable material price variance?
JKI is planning a golfing holiday for a group of wealthy lawyers.
The lawyers will fly to the local airport at their own expense. JKI will then pay for transport, accommodation and the use of the golf course (green fees).
JKI's costings are as follows, based on 28 participants:
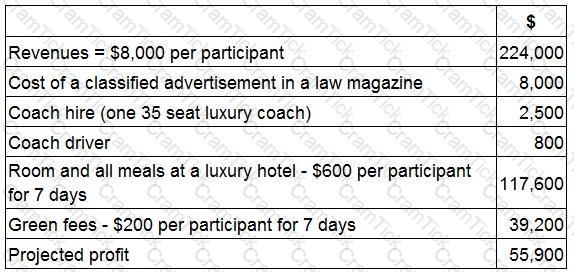
JKI received 46 applications from potential participants.
What would the profit be if JKI accepted all of these bookings?
Give your answer to the nearest whole number.
A company makes a product using two materials, X and Y.
The standard materials required for one unit of the product are:

What is the direct material mix variance for Material X, using the individual valuation basis?
The simplex method has been used to determine the optimum output of products P, Q, R and S with constraints on resources J, K and L.
In the final simplex tableau, the figure in the product R row and the column for slack variable K is 80.
Which of the following statements is correct?
The following details are available for a company's production overhead costs at different levels of activity:
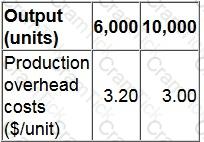
The company uses the high-low method to calculate its budgeted production overhead costs.
What is the budget for production overhead costs at an activity level of 8,500 units?
Give your answer as a whole number.
The manager of a recently opened cafe is deciding how many sandwiches to make each day.
The sandwiches are made in the morning before the cafe opens.
If demand exceeds the number of sandwiches made in the morning no extra sandwiches can be made during the day. Any unsold sandwiches are thrown away at the end of each day.
Daily demand is uncertain but is predicted to be 10, 20, 30 or 40 sandwiches.
The following regret matrix has been prepared:
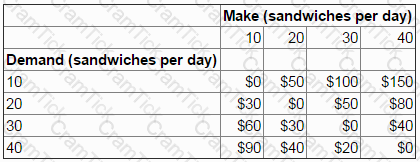
If the minimax regret criterion is used to make the decision, the manager will choose to make:
Changing to a just-in-time, from a traditional, manufacturing environment can affect cost accounting systems.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A company sells and services photocopying machines. Its sales department sells the machines and consumables, including ink and paper, and its service department provides an after sales service to its customers. The after sales service includes planned maintenance of the machine and repairs in the event of a machine breakdown. Service department customers are charged an amount per copy that differs depending on the size of the machine.
The company’s existing costing system uses a single overhead rate, based on total sales revenue from copy charges, to charge the cost of the Service Department’s support activities to each size of machine. The Service Manager has suggested that the copy charge should more accurately reflect the costs involved. The company’s accountant has decided to implement an activity-based costing system and has obtained the following information about the support activities of the service department:
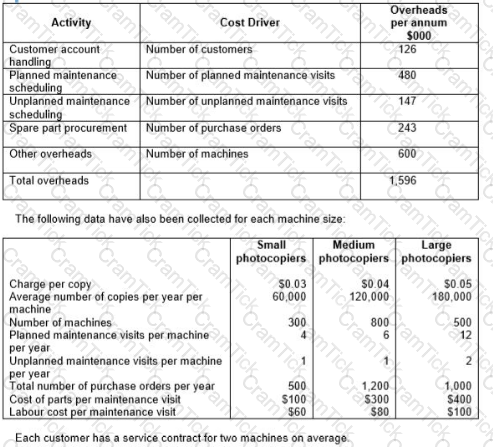
Calculate the annual profit per machine for each of the three sizes of machine, using the current basis for charging the costs of support activities to machines.
Christian the management accountant at a car manufacturer has been given a list of costs that have been incurred due to accidents and errors either occurring or being prevented.
Which of the following are examples of non-conformance costs? Select ALL that apply.
The inventory level of Product Y has reduced by 40 units over a single period. The cost card for Product Y is as follows:
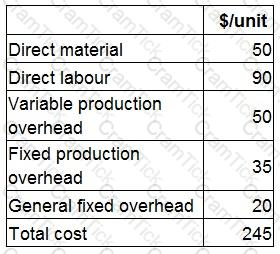
The profit for Product Y using marginal costing is $26,000.
If the company used absorption costing, what would the profit for Product Y be?
Give your answer to the nearest whole $.
An agricultural company uses activity based costing to charge overheads to its three products. One of the main activities is purchasing, budgeted details of which are as follows:
Additional budgeted data:

What is the budgeted purchasing overhead cost per kg of Product S?
Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Information about a company's only two products is as follows:
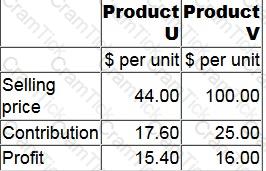
The revenue from the products must be in the constant mix of 2U:3V. Budgeted monthly sales revenue is $110,000.
Fixed costs are $23,095 each month.
To the nearest $10, what is the budgeted monthly margin of safety in terms of sales revenue?
A company makes two products, product X with a contribution per unit of $10 and product Y with a contribution per unit of $4.
These products are sold in the mix 3:2 by volume and fixed costs are $38,000 per period.
The breakeven point for product Y, based on the expected sales mix is:
A major company sells a range of electrical, clothing and homeware products through a chain of department stores. The main administration functions are provided from the company’s head office. Each department store has its own warehouse which receives goods that are delivered from a central distribution center.
The company currently measures profitability by product group for each store using an absorption costing system. All overhead costs are charged to product groups based on sales revenue. Overhead costs account for approximately one-third of total costs and the directors are concerned about the arbitrary nature of the current method used to charge these costs to product groups.
A consultant has been appointed to analyses the activities that are undertaken in the department stores and to establish an activity based costing system.
The consultant has identified the following data for the latest period for each of the product groups for the X Town store:
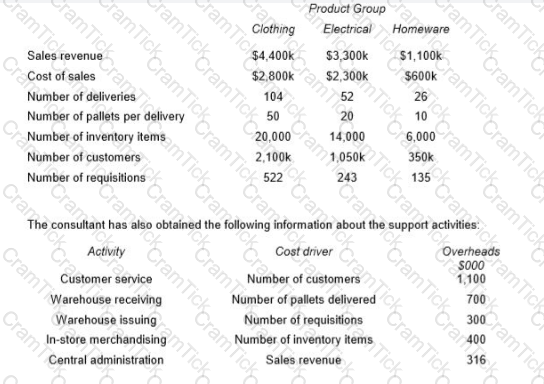
Calculate the total profit for each of the product groups:
…. using the current absorption costing system;
A company uses a standard costing system.
The company’s sales budget for the latest period includes 1,500 units of a product with a selling price of $400 per unit.
The product has a budgeted contribution to sales ratio of 30%.
Actual sales for the period were 1,630 units at a selling price of $390 per unit.
The actual contribution to sales ratio was 28%.
The sales volume contribution variance for the product for the latest period is:
A company’s management is considering investing in a project with an expected life of 4 years. It has a positive net present value of $180,000 when cash flows are discounted at 8% per annum. The project’s cash flows include a cash outflow of $100,000 for each of the four years. No tax is payable on projects of this type.
The percentage increase in the annual cash outflow that would cause the company’s management to reject the project from a financial perspective is, to the nearest 0.1%: