According to Basel II's definition of operational loss event types, losses due to acts by third parties intended to defraud, misappropriate property or circumvent the law are classified as:
When modeling operational risk using separate distributions for loss frequency and loss severity, which of the following is true?
An operational loss severity distribution is estimated using 4 data points from a scenario. The management institutes additional controls to reduce the severity of the loss if the risk is realized, and as a result the estimated losses from a 1-in-10-year losses are halved. The 1-in-100 loss estimate however remains the same. What would be the impact on the 99.9th percentile capital required for this risk as a result of the improvement in controls?
For the purposes of calculating VaR, an interest rate swap can be modeled as a combination of:
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Top down approaches help focus management attention on the frequency and severity of loss events, while bottom up approaches do not.
II. Top down approaches rely upon high level data while bottom up approaches need firm specific risk data to estimate risk.
III. Scenario analysis can help capture both qualitative and quantitative dimensions of operational risk.
A Monte Carlo simulation based VaR can be effectively used in which of the following cases:
Which of the following are valid criticisms of value at risk:
I. There are many risks that a VaR framework cannot model
II. VaR does not consider liquidity risk
III. VaR does not account for historical market movements
IV. VaR does not consider the risk of contagion
If EV be the expected value of a firm's assets in a year, and DP be the 'default point' per the KMV approach to credit risk, and σ be the standard deviation of future asset returns, then the distance-to-default is given by:
A)

B)
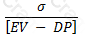
C)
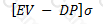
D)
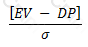
The backtesting of VaR estimates under the Basel accord requires comparing the ex-ante VaR to:
Under the contingent claims approach to measuring credit risk, which of the following factors does NOT affect credit risk:
A key problem with return on equity as a measure of comparative performance is:
A statement in the annual report of a bank states that the 10-day VaR at the 95% level of confidence at the end of the year is $253m. Which of the following is true:
I. The maximum loss that the bank is exposed to over a 10-day period is $253m.
II. There is a 5% probability that the bank's losses will not exceed $253m
III. The maximum loss in value that is expected to be equaled or exceeded only 5% of the time is $253m
IV. The bank's regulatory capital assets are equal to $253m
When the volatility of the yield for a bond increases, which of the following statements is true:
What is the 1-day VaR at the 99% confidence interval for a cash flow of $10m due in 6 months time? The risk free interest rate is 5% per annum and its annual volatility is 15%. Assume a 250 day year.
Which of the following would not be a part of the principal component structure of the term structure of futures prices?
The returns for a stock have a monthly volatilty of 5%. Calculate the volatility of the stock over a two month period, assuming returns between months have an autocorrelation of 0.3.
For a group of assets known to be positively correlated, what is the impact on economic capital calculations if we assume the assets to be independent (or uncorrelated)?
There are three bonds in a diversified bond portfolio, whose default probabilities are independent of each other and equal to 1%, 2% and 3% respectively over a 1 year time horizon. Calculate the probability that none of the three bonds will default.
Which of the following statements are true:
I. Credit VaR often assumes a one year time horizon, as opposed to a shorter time horizon for market risk as credit activities generally span a longer time period.
II. Credit losses in the banking book should be assessed on the basis of mark-to-market mode as opposed to the default-only mode.
III. The confidence level used in the calculation of credit capital is high when the objective is to maintain a high credit rating for the institution.
IV. Credit capital calculations for securities with liquid markets and held for proprietary positions should be based on marking positions to market.
Which of the following statements is true:
I. Recovery rate assumptions can be easily made fairly accurately given past data available from credit rating agencies.
II. Recovery rate assumptions are difficult to make given the effect of the business cycle, nature of the industry and multiple other factors difficult to model.
III. The standard deviation of observed recovery rates is generally very high, making any estimate likely to differ significantly from realized recovery rates.
IV. Estimation errors for recovery rates are not a concern as they are not directionally biased and will cancel each other out over time.
Assuming all other factors remain the same, an increase in the volatility of the returns on the assets of a firm causes which of the following outcomes?
Which of the following risks and reasons justify the use of scenario analysis in operational risk modeling:
I. Risks for which no internal loss data is available
II. Risks that are foreseeable but have no precedent, internally or externally
III. Risks for which objective assessments can be made by experts
IV. Risks that are known to exist, but for which no reliable external or internal losses can be analyzed
V. Reducing the complexity of having to fit statistical models to internal and external loss data
VI. Managing the capital estimation process as to produce estimates in line with management's desired capital buffers.
A bank prices retail credit loans based on median default rates. Over the long run, it can expect:
If the annual variance for a portfolio is 0.0256, what is the daily volatility assuming there are 250 days in a year.
In the case of historical volatility weighted VaR, a higher current volatility when compared to historical volatility:
What is the risk horizon period used for credit risk as generally used for economic capital calculations and as required by regulation?
Which of the following are true:
I. Monte Carlo estimates of VaR can be expected to be identical or very close to those obtained using analytical methods if both are based on the same parameters.
II. Non-normality of returns does not pose a problem if we use Monte Carlo simulations based upon parameters and a distribution assumed to be normal.
III. Historical VaR estimates do not require any distribution assumptions.
IV. Historical simulations by definition limit VaR estimation only to the range of possibilities that have already occurred.
Which of the following is a measure of the level of capital that an institution needs to hold in order to maintain a desired credit rating?
Which of the following will be a loss not covered by operational risk as defined under Basel II?
A stock's volatility under EWMA is estimated at 3.5% on a day its price is $10. The next day, the price moves to $11. What is the EWMA estimate of the volatility the next day? Assume the persistence parameter λ = 0.93.
Under the CreditPortfolio View approach to credit risk modeling, which of the following best describes the conditional transition matrix:
For credit risk calculations, correlation between the asset values of two issuers is often proxied with:
If the full notional value of a debt portfolio is $100m, its expected value in a year is $85m, and the worst value of the portfolio in one year's time at 99% confidence level is $60m, then what is the credit VaR?
If the 99% VaR of a portfolio is $82,000, what is the value of a single standard deviation move in the portfolio?
Which of the following statements are correct:
I. A training set is a set of data used to create a model, while a control set is a set of data is used to prove that the model actually works
II. Cleansing, aggregating or ensuring data integrity is a task for the IT department, and is not a risk manager's responsibility
III. Lack of information on the quality of underlying securities and assets was a major cause of the collapse in the CDO markets during the credit crisis that started in 2007
IV. The problem of lack of historical data can be addressed reasonably satisfactorily by using analytical approaches
For a back office function processing 15,000 transactions a day with an error rate of 10 basis points, what is the annual expected loss frequency (assume 250 days in a year)
Which of the following statements are true?
I. Retail Risk Based Pricing involves using borrower specific data to arrive at both credit adjudication and pricing decisions
II. An integrated 'Risk Information Management Environment' includes two elements - people and processes
III. A Logical Data Model (LDM) lays down the relationships between data elements that an organization stores
IV. Reference Data and Metadata refer to the same thing
The capital adequacy ratio applied to risk weighted assets for the calculation of capital requirements for credit risk per Basel II is:
Between two options positions with the same delta and based upon the same underlying, which would have a smaller VaR?
If F be the face value of a firm's debt, V the value of its assets and E the market value of equity, then according to the option pricing approach a default on debt occurs when:
There are three bonds in a diversified bond portfolio, whose default probabilities are independent of each other and equal to 1%, 2% and 3% respectively over a 1 year time horizon. Calculate the probability that exactly 1 of the three bonds will default.
Which of the following are valid approaches to calculating potential future exposure (PFE) for counterparty risk:
I. Add a percentage of the notional to the mark-to-market value
II. Monte Carlo simulation
III. Maximum Likelihood Estimation
IV. Parametric Estimation
A corporate bond has a cumulative probability of default equal to 20% in the first year, and 45% in the second year. What is the monthly marginal probability of default for the bond in the second year, conditional on there being no default in the first year?
If an institution has $1000 in assets, and $800 in liabilities, what is the economic capital required to avoid insolvency at a 99% level of confidence? The VaR in respect of the assets at 99% confidence over a one year period is $100.
There are two bonds in a portfolio, each with a market value of $50m. The probability of default of the two bonds over a one year horizon are 0.03 and 0.08 respectively. If the default correlation is zero, what is the one year expected loss on this portfolio?
The largest 10 losses over a 250 day observation period are as follows. Calculate the expected shortfall at a 98% confidence level:
20m
19m
19m
17m
16m
13m
11m
10m
9m
9m
PRM Certification | 8008 Questions Answers | 8008 Test Prep | PRM Certification - Exam III: Risk Management Frameworks, Operational Risk, Credit Risk, Counterparty Risk, Market Risk, ALM, FTP - 2015 Edition Questions PDF | 8008 Online Exam | 8008 Practice Test | 8008 PDF | 8008 Test Questions | 8008 Study Material | 8008 Exam Preparation | 8008 Valid Dumps | 8008 Real Questions | PRM Certification 8008 Exam Questions


