The underlying pathophysiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is best explained as
A patient with an acute anterior wall MI presents with an S3 gallop and the following values:
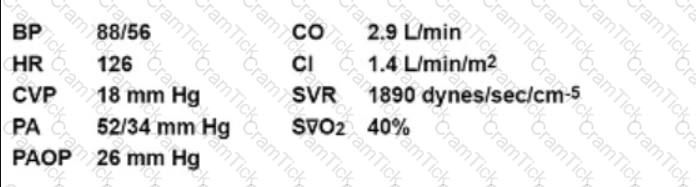
Which drug therapy would be most appropriate for this patient?
A terminally ill patient is deteriorating. The patient's family states, "We don't want him to suffer any more." The most appropriate response is
A patient who underwent bowel resection surgery due to small bowel rupture is tachycardic and hypotensive. A nurse calls the on-call surgical resident and reports the findings. No new orders are received. The nurse should continue to monitor the patient and
A nurse is providing care to a patient diagnosed with abdominal compartment syndrome. The nurse should recognize the patient is most at risk for developing
The family member of a patient who is receiving mechanical ventilation is to be taught suctioning. When developing a teaching plan, the nurse should first
Family members have been complaining about limited visiting hours. To facilitate a potential change in practice, a nurse should first
An unconscious patient in hepatic failure secondary to alcoholism becomes acutely hypoglycemic. Glucagon administration is contraindicated for this patient because glucagon
Which of the following assessment findings would be found in a patient with pulmonary hypertension?
Which of the following diagnostic procedures best pinpoints the location, size, and origin of a cerebral aneurysm?
An older adult patient is admitted with acute exacerbation of congestive heart failure. An echocardiogram indicates that EF is unchanged at 50%. The patient is most likely experiencing
In a patient with status asthmaticus, which of the following indicate a deteriorating condition?
A nurse is caring for a patient with pulmonary fibrosis who is exhibiting shortness of breath, tachypnea, and feels a sense of impending doom. In order to relieve these symptoms, the nurse should anticipate an order for
A patient is admitted with Gl bleeding. During the assessment, the nurse notes the patient to be tremulous, anxious, and startles every time he is touched by the nurse. Which of the following is the most pertinent part of the patient's history to obtain?
A patient who is confused and dyspneic is admitted with ABG values that reveal hypoxemia. Results from insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter are:
PAP 38/18 mm Hg
PAOP10 mm Hg
CI 3.5 L/min/m2
These values are most indicative of
A patient with unilateral facial droop and slurred speech has a history of hyperlipidemia and hypertension. The nurse should anticipate an order for a
A nurse is performing medication reconciliation during a patient's admission. To determine the patient's current understanding of the medication furosemide (Lasix), which of the following is the best statement by the nurse?
To maintain adequate pain control in a post-surgical patient addicted to heroin, a nurse should plan to
A patient with a C5 spinal cord injury calls the nurse every 15 minutes with requests for juice, water, and repositioning. Which of the following is the nurse's best response?
A patient is intubated and receiving assist control mechanical ventilation and is on a norepinephrine drip following a head injury. Patient data are:

Which of the following interventions will improve cerebral perfusion?
Which of the following serum laboratory results is most concerning to a nurse who is caring for a patient with a Stage Ill pressure ulcer on the coccyx?
A patient is admitted with anaphylactic shock secondary to a blood transfusion. The patient's spouse asks the nurse to explain how blood can cause a low blood pressure. The nurse responds that with anaphylactic shock the
The spouse of a critically ill patient is indecisive, withdrawn, and tells the nurse, "I feel so helpless." Appropriate nursing interventions include
Patients in end-stage cardiomyopathy often exhibit which of the following symptoms of right-sided heart failure?
A patient is admitted for sepsis secondary to pneumonia. The patient has received 2000 mL of plasmalyte and their BP remains 80/50. What should the nurse anticipate next for the patient?
In a patient with a chest tube, an air leak in the pleural space is indicated by which of the following conditions in the water-seal chamber?
When assessing a patient who has acute pancreatitis, which of the following findings require immediate notification to the provider?
A patient is admitted with a traumatic brain injury. During assessment, a nurse notes increased urinary output from the catheter. Which of the following should the nurse suspect?
The nurse who is caring for a patient following an esophagectomy notes new subcutaneous emphysema in the upper chest and neck. The nurse should expect an order for
A patient's blood culture report notes the presence of vancomycin resistant enterococcus. The nurse should place the patient in which type of isolation?
The family of a patient requests permission to administer traditional herbs to the patient. Which of the following should be the nurse's first action?
A patient is 2 days post MI. The patient was stable until this morning, when severe chest discomfort developed. Assessment reveals:
BP70/palpable
HR122
RR38
PAOP28 mm Hg, with large V waves
CI1.6 L/min/m2
Cool, clammy skin
Inspiratory crackles throughout the lung field
Loud blowing holosystolic murmur at the apex
The patient's present clinical status is most likely a result of
A patient has gained 8 kg in the past week. Serum sodium is 115 mEq/L, CVP is 20 mm Hg, and serum osmolality is decreased. The patient has just experienced a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. In this situation, which of the following IV solutions should a nurse be prepared to administer?
During the monthly code team review, it is noted that regulators have been consistently missing from the O2 tanks. Which of the following is a nurse's best action?
A patient with cardiogenic shock for several days has been managed aggressively with vasopressor and inotrope therapies. Which of the following indicates organ dysfunction from hypoperfusion?
CCRN |


